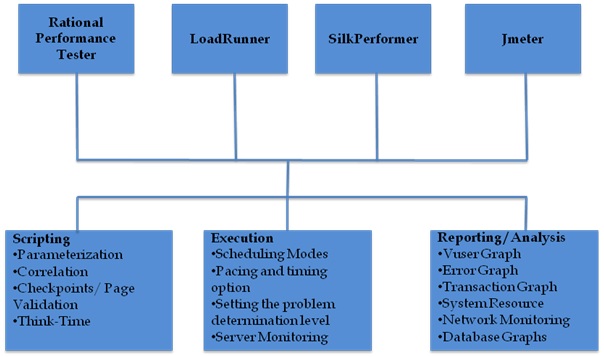
To
do correlation in LoadRunner we need both Left Boundary and Right Boundary of
the dynamic value which we are planning to capture, but if there is a situation
where boundaries are also dynamic..?
Technique
to do correlation when boundaries are dynamic
For
complex changes, we first capture a subset of the server response, based on some
unique boundaries identified, and then with the aid of custom built-in Text
Flags in the correlation functions, we get the desired substring out of
the captured string.
Simple
solution for this is to use “Text Flags”,
where I provide you with few different scenarios with solutions
Type 1:
Consider
that you have a situation where you need to capture text/string DynamicValue, but the problem here is
left boundary of the string changing every time you replay. For e.g. you get
the left boundary as abcXdef, where X ranges between 0 and 9 as
abc0def=DynamicValueRight Boundary
abc1def=DynamicValueRight Boundary
abc2def=DynamicValueRight Boundary
-
-
-
-
abc9def=DynamicValueRight Boundary
Solution:
To capture the desired
text/string, we can put the following by modifying the correlation function argument with
the text flag as **/DIG, where
for the above scenario we need to place LB/DIG argument as shown below
web_reg_save_param(“Param_Name”,”LB/DIG= abc#def\=”,”RB=Right Boundary”,LAST);
Note: The dynamic values in
boundaries are replaced with #
symbol.
Type 2:
If
the dynamic values are of below scenario
abc013def=DynamicValueRight Boundary
abc122def=DynamicValueRight Boundary
abc232def=DynamicValueRight Boundary
-
-
-
-
abc906def=DynamicValueRight Boundary
Solution:
In
the given scenario there are multiple digits which are randomly changing, so we
have to place the # sign for each random digit.
web_reg_save_param(“Param_Name”,”LB/DIG= abc###def\=”,”RB=Right Boundary”,LAST);
Type 3:
If
the dynamic boundaries are of below type (Alpha numeric)
abc0c3def=DynamicValueRight Boundary
abc1h2def=DynamicValueRight Boundary
abcn3edef=DynamicValueRight Boundary
-
-
-
-
Abcz46def=DynamicValueRight Boundary
Solution:
In
the given scenario the left boundary values are dynamic with different alpha
numeric values, so we need to place the sign ^ instead of #, by
modifying the correlation function argument as **/ALNUM instead of **/DIG text
flag with the desired boundary argument.
web_reg_save_param(“Param_Name”,”LB/DIG= abc^^^def\=”,”RB=Right Boundary”,LAST);
Type 4:
If
the boundaries are containing case sensitive nature
Solution:
Whenever
there is a nature of case sensitive, we
need to modify the correlation function argument as **/IC/DIG text flag with the desired boundary arguments as below
web_reg_save_param(“Param_Name”,”LB/IC/DIG= abc#def\=”,”RB=Right Boundary”,LAST);
Below
is the list of text flags that LoadRunner can support
Argument
|
Description
|
/IC
|
To ignore the case
type
|
/BIN
|
To specify the
binary data
|
/DIG
|
To interpret the
sign # as a wildcard for a single digit
|
/ALNUM
|
To interpret the
sign ^ as a wildcard for a single alpha numeric type
|